Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has transformed the landscape of molecular biology, enabling rapid, high-throughput analysis of genetic material. From prenatal diagnostics to agricultural applications, NGS technology facilitates detailed genetic analysis, assisting in diagnosing genetic diseases, selecting quality breeds, and even supporting scientific research in universities and industrial laboratories. In this blog, we explore the diverse applications of NGS technology, the specific requirements of various customer groups, and the importance of robust library construction tools in achieving successful outcomes.
1. NGS in Prenatal Diagnostics and Genetic Disease Detection
NGS is widely adopted in prenatal diagnostics and genetic disease detection, providing precise insights into genetic abnormalities early on. This field typically serves two main customer groups:
- IVD Companies and Medical Inspection Centers: These institutions have the necessary medical qualifications to conduct diagnostic tests for genetic conditions.
- Hospitals: Many hospitals with in-house laboratories perform NGS-based diagnostics for prenatal testing and genetic disease screening.
Samples and Automation: Blood and body fluids are the primary sample types for genetic testing in prenatal diagnostics. While there is some level of automation in library construction for these tests, a significant portion still requires manual handling due to the specific protocols of each institution.
Product Requirements: The primary demand is for DNA library construction kits, with some applications requiring multiplex amplification and single-cell genome amplification for precise analysis.
Process Adaptation: While NGS technology integrates well into existing workflows, some customization is often required to ensure compatibility with each institution’s protocols, particularly in more specialized medical laboratories.
2. NGS for Agricultural Breeding and Quality Selection
In agriculture, NGS technology aids in selecting high-quality breeds and improving genetic diversity in crops and livestock. Customer groups in this domain include:
- Breeding Services Companies: These entities, including major corporations, utilize NGS to identify desirable genetic traits.
- Breeding Industry Corporations: Major agricultural companies leverage NGS to improve crop and livestock quality.
- Certification and Inspection Units: Agencies that inspect livestock and crop genetics rely on NGS for accurate genetic profiling.
Sample Types: Agricultural applications mainly involve single sample types from specific species, such as cattle, sheep, rice, and corn, focusing on a uniform evaluation system.
High Automation in Library Construction: Unlike clinical applications, agricultural NGS processes often involve a higher level of automation, as companies deal with large numbers of samples and require consistent data for quality control.
Product Needs: DNA and RNA library construction kits are essential, with a focus on high success rates in sequencing. For companies focusing on RNA analysis, additional tools are necessary for the quantification and verification of genetic traits.
3. Scientific Research and Publication: Expanding the Boundaries of Knowledge
Universities, scientific research units, and research institutions extensively utilize NGS for diverse studies, from studying plant genetics to analyzing microbial communities in various ecosystems. Customer groups include:
- Scientific Research Units and Universities: These institutions rely on NGS for exploratory studies, often requiring flexibility in sample types and methodologies.
- Research Outsourcing Services: Some scientific institutions outsource sequencing and data analysis to third-party NGS service providers.
Sample Diversity and Universal Compatibility: Unlike other applications, research institutions handle a wide variety of samples, including plant, animal, blood, and soil samples. Thus, NGS products in this domain must offer universal compatibility across different sample types and be adaptable to various protocols.
Automation and Database Building: With large sample volumes, research institutions emphasize automation in database construction, reagent consistency, and ease of use. These institutions often experiment with streamlined processes to reduce manual labor.
Product Requirements: Research applications necessitate versatile DNA and RNA library construction kits, with customization options for specialized studies. Apparent library construction kits may also be used, offering researchers a universal toolkit adaptable to different sample types and experiment goals.
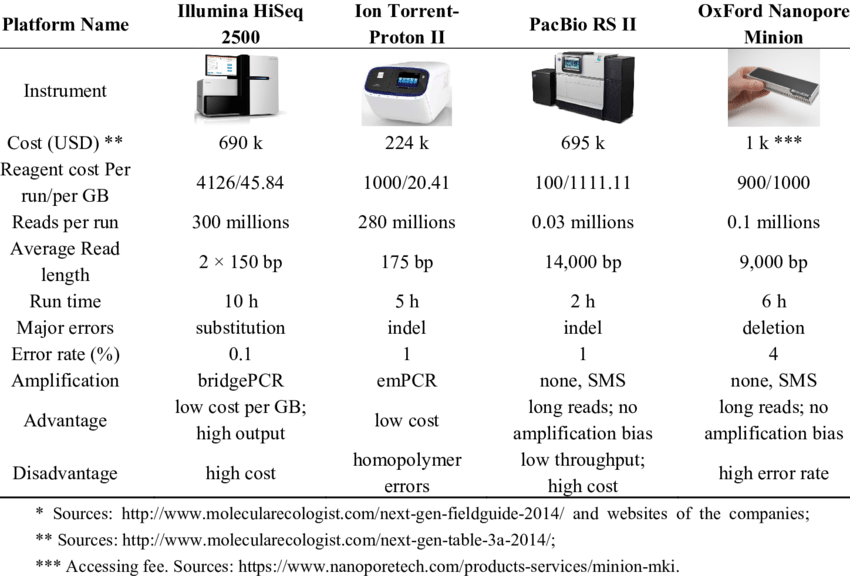
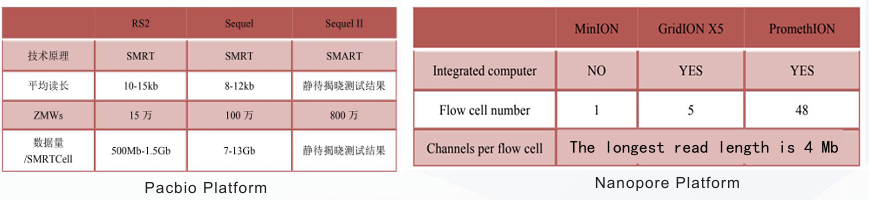
4. Key Platforms Supporting NGS Technology
NGS platforms like PacBio and Nanopore provide unique capabilities for sequencing. Each platform has strengths that serve specific research needs:
- PacBio Platform: Known for long-read sequencing, the PacBio system offers high accuracy and is suitable for complex genomic applications. It includes models like the RS2 and Sequel series, with capabilities ranging from 10-15 kb read lengths to a maximum of 1.5 Gb per SMRT cell.
- Nanopore Platform: Known for scalability, the Nanopore platform (e.g., MinION, GridION, PromethION) provides real-time sequencing capabilities with the ability to achieve read lengths up to 4 Mb, allowing flexibility in sequencing large genomes.
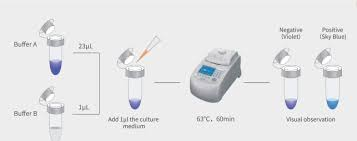
5. Meeting Specific Standards with MycAway® Mycoplasma Detection Kit
In the realm of contamination control, Yeasen Bio's MycAway® Mycoplasma Real-time qPCR Detection Kit stands out for its reliability and compliance with pharmacopoeia standards. This kit is tailored for the qualitative detection of mycoplasma DNA, ensuring that researchers and clinical labs can detect contamination accurately.
Features:
- Comprehensive Components: The kit includes buffers, primers, probes, and positive/negative controls, making it a complete solution for contamination screening.
- Wide Compatibility: Suitable for multiple PCR platforms, including Thermo’s ABI 7500 and Bio-Rad’s CFX96, ensuring broad applicability.
- High Detection Sensitivity: The kit meets the stringent detection limit of 10 CFU/mL, allowing for reliable detection even at low contamination levels.
6. Ensuring Reliability with Comprehensive Testing Standards
MycAway® kits undergo rigorous quality control to ensure reliable results in various conditions. Testing includes:
- Sequence Consistency: Ensures the probe sequence aligns with genomic sequences.
- Sample Matrix Interference: Verifies that common sample matrices do not affect results.
- Durability: Assesses kit stability across freeze-thaw and heat-accelerated conditions.
This meticulous approach to quality control helps ensure that laboratories can trust the MycAway® kit for accurate, repeatable results in detecting mycoplasma contamination.
Conclusion
The versatility of NGS technology in diagnostics, agriculture, and research demonstrates its transformative impact across multiple sectors. From prenatal diagnostics to scientific research, each application of NGS presents unique challenges and opportunities, which companies like Yeasen Bio address with advanced library construction kits and contamination control products.
The strategic integration of platforms like PacBio and Nanopore further broadens the scope of NGS applications, enabling researchers to tackle increasingly complex genetic questions. As NGS technology continues to advance, products that offer high precision, adaptability, and quality assurance will remain central to supporting groundbreaking discoveries in genetics.